To calculate result you have to disable your ad blocker first.
Addends in Mathematics: Definition, Types, and Examples
Publish Date: 08 Aug, 2023
Table of Content
The term “Addends” is commonly used in mathematics to refer to the numbers that are added together to find a sum. The modern notation and terminology for addition, including the use of the term “addends,” began to take shape in the Middle Ages and Renaissance.
In this article, we will discuss the basic concept of addends, understand the procedure of addends, and solve some examples for better understanding.
What are Addends?
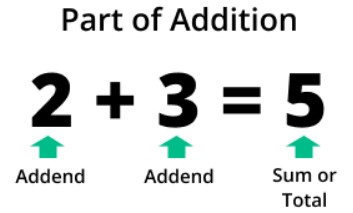
Addends are the individual numbers/terms that are being added together in an addition operation to obtain a sum. In a simple addition equation, such as "2 + 3 = 5," the numbers "2" and "3" are the addends.
They are the quantities or values that are combined through the addition process to produce the total or sum, which in this case is "5."
Addends can be positive or negative numbers, fractions, decimals, or even algebraic terms. Regardless of the specific numerical values or variables involved, addends are the components that are being added together to find the result.
Types of Addends
Addends can take forms depending on the context in which they are used. Here are some common types of addends:
- Integers are whole numbers also used as addends. For example, in the equation “
4 + 7 = 11,” both “4” and “7” are whole number addends. - Fractions represent a part of a whole and consist of a numerator and a denominator separated by a slash. In the equation “1
/4 + 3/8 = 5/8,” “1/4” and “3/8” are fraction addends. - Negative numbers are numbers less than zero and are typically represented with a minus sign (-) before the number. In the equation “
-6 + 3 = -3,” “-6” and “3” and negative addends. - In algebraic expressions, variables are used to represent unknown values. For example, in the equation “
x + 5 = 10,” “x” and “5” are the addends, with “x” representing an unknown value. - Decimals are numbers that include a decimal point to represent a fractional part of a whole number. In equation “
2.5 + 1.75 = 4.25,” “2.5” and “1.75” are decimal addends.
Properties of Addends
Addends are influenced by specific mathematical rules that need to be followed when solving problems.
- The commutative property
- The associative property
- The additive identity property
- The additive inverse property
- The closure property
The commutative property:
The commutative property states that the order of addition of the addends cannot be changed in the final result. For example, for any “a” and “b”, a + b = b + a
The associative property:
The associative property states that the order of addition of addends does not make a change in the final result. For example, for any numbers “a”, “b”, and “c”, (a + b) + c = a + (b + c).
The additive identity property:
The identity property of addition states that there exists a unique number, called the additive identity, which, when added to any number, leaves the number unchanged. We know that “The additive identity for addition is 0”. For any number “a”, a + 0 = 0 + a = a.
The additive inverse property:
The inverse property of addition states that for every number, there exists a unique additive inverse that, when added together, yields the additive identity (0). For any number “a”, a + (-a) = (-a) + a = 0.
The closure property:
The closure property of addition states that when adding two numbers, the result is always a number within the same set of numbers. For example, if “a” and “b” are real numbers then a + b is also a real number.
Examples of Addends
Here we can express some examples of addends to understand the basic concept and phenomena of addends.
Example 1:
In addition to “5 + 6 = 11” identify the addends.
Solution:
Here we have “5 + 6 = 11” as the question of addition.
In addition, involving numbers are called addends.
So, here “5” and “6” are involved in addition so these two numbers are called addends in this question.
Example 2:
If you have 4 chocolates and your father, gives you 11 more, how many chocolates do you have? Also, identify addends.
Solution:
You have 4 chocolates then your father gives you 11 more. So,
4 + 11 = 15
Now you have 15 chocolates.
In addition, numbers involved in addition are “4” and “11” these are called addends.
Wrap up
Addends are numbers involving addition, here we analyzed the history of addends and understand the basic concept and who and when the first time give the idea of addends. We also discuss the types and properties of addends with examples

